What Is WiFi and How It Works?
In our modern world, WiFi has become an essential aspect of daily life, providing the convenience of wireless internet access in homes, offices, cafes, and public spaces. But what exactly is WiFi, and how does it work? This article aims to demystify WiFi technology, exploring its components, functioning, and how it has revolutionized the way we connect to the internet.
What is WiFi?
WiFi, short for Wireless Fidelity, refers to a technology that allows devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smart home appliances to connect to the internet without the need for physical cables. It operates under a set of standards developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), specifically the 802.11 family of standards.
WiFi uses radio waves to transmit data between devices and a router, which is connected to the internet. This enables users to access the web from anywhere within the coverage area of the WiFi network.
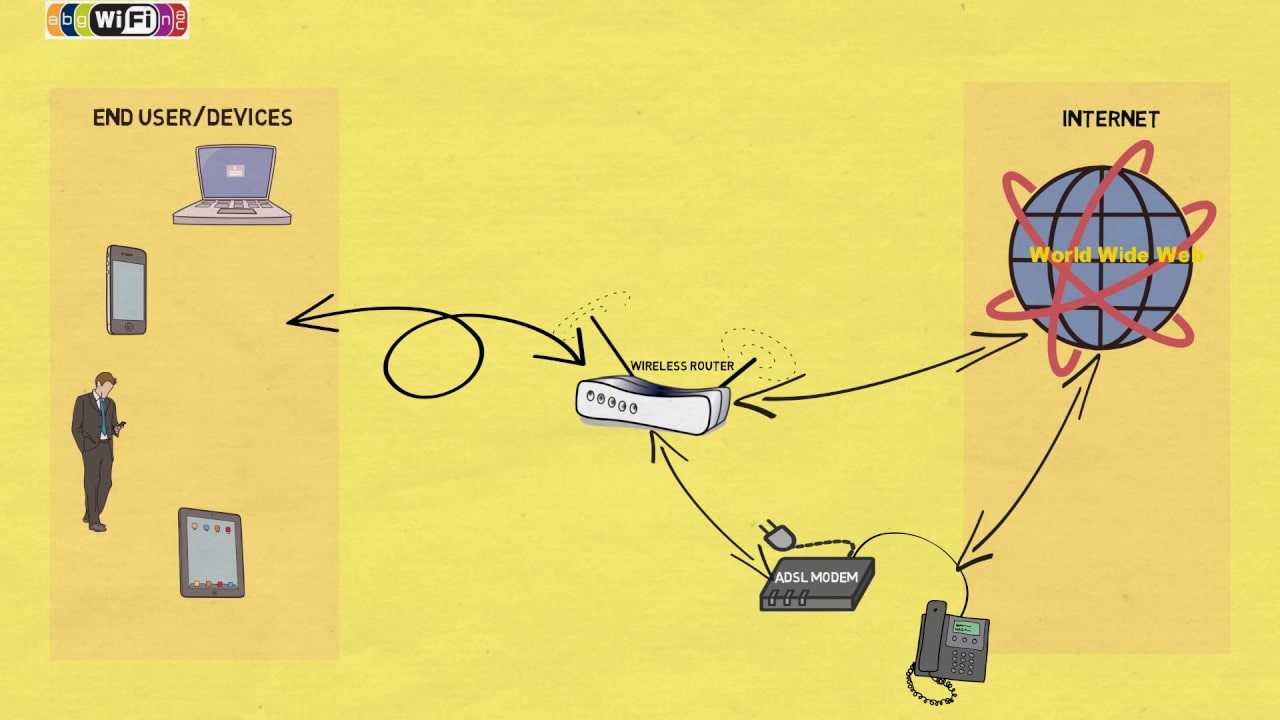
How WiFi Works
Understanding how WiFi works involves a few key components:
- Wireless Router: The backbone of any WiFi network, the wireless router acts as a central hub. It connects to the internet through a modem and transmits data wirelessly to connected devices. Routers use various technologies to enable efficient transmission, including multiple antennas and advanced protocols.
- WiFi Standards: WiFi operates on different standards based on the 802.11 protocols. These standards dictate the speed and range of wireless connections. Common standards include:
- 802.11n: Offers speeds of up to 600 Mbps, using both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- 802.11ac: Known as WiFi 5, it supports higher speeds (up to 3.5 Gbps) and improved performance in crowded environments.
- 802.11ax: Known as WiFi 6, it brings even more advancements in speed, capacity, efficiency, and reduced latency, especially for high-density environments.
- Radio Waves: WiFi technology utilizes electromagnetic radiation in the form of radio waves to transmit data. These waves operate on specific frequency bands—primarily 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band offers broader coverage but is often slower and more prone to interference. The 5 GHz band provides faster speeds but has a shorter range.
- Client Devices: Devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smart TVs come equipped with WiFi adapters that allow them to connect to the router. These adapters convert the radio signals being transmitted into data that the device can understand and vice versa.
The Process of WiFi Communication
Here’s a simplified overview of how WiFi communication occurs:
- Connecting Devices: When a device, such as a smartphone, wants to connect to the internet, it searches for available WiFi networks and displays them for the user.
- Establishing a Connection: Once the user selects a network and inputs the password (if required), the device sends a request to the router.
- Data Transmission: Upon successful authentication, a secure connection is established. The router assigns an Internet Protocol (IP) address to the device and begins relaying data. The device sends data packets to the router, which then forwards them to the internet, and the response is sent back to the router to the device.
- Signal Modulation: The data transmitted is encoded in binary and sent as radio waves. Modulation techniques, like Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), further enhance the speed and capacity of data transfer.
The Benefits of WiFi
WiFi technology has transformed how we access and use the internet. Here are some of its key benefits:
- Convenience: WiFi allows users to connect multiple devices without the clutter of cables, enabling mobility and flexibility in how we access the internet.
- Accessibility: WiFi provides access to the internet in various environments, from homes to public spaces like cafes, parks, and airports.
- Scalability: Setting up a WiFi network can easily accommodate multiple devices, making it particularly suited for homes and businesses.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many internet service providers offer affordable WiFi plans, making internet access accessible for a wide range of users.
Challenges and Considerations
While WiFi offers numerous advantages, there are also challenges:
- Interference: WiFi signals can be affected by physical obstructions (walls or furniture) and electronic devices (microwaves, cordless phones), leading to reduced performance.
- Security Risks: Public WiFi networks can be vulnerable to hackers. It's crucial to use secure connections (VPNs, HTTPS websites) when accessing sensitive information.
- Limited Range: WiFi signals decrease in strength with distance from the router, which can create dead zones in larger homes or buildings.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi technology has revolutionized our ability to connect to the internet, offering convenience and accessibility in a wireless format. Understanding how WiFi works and its underlying principles can help users optimize their networks and enhance their online experience. Whether at home or on the go, WiFi continues to be a vital part of our digital lives, enabling seamless connectivity and communication in an increasingly interconnected world.